Compression Limiters
Compression limiters are often used when an application includes a plastic assembly which has a compressive load to bear. The compression limiter strengthens the assembly and takes on the load that is applied when a bolt is tightened within the assembly. When a compression limiter is used, the plastic's integrity is not compromised by the added pressure.
CUSTOM MANUFACTURING
Custom Compression Limiters
We produce custom compression limiters designed to exact specifications for a variety of industries and applications. We can produce various lengths and overall sizes to accommodate both U.S. and metric bolts.
All that's needed to create a custom compression limiter is your design type, material preference, part length, ID, OD, installation method, and if you require a plating of finish. More details about these manufacturing specifications are listed below.
To customize a compression limiter or send us your design and specifications, request a custom quote.
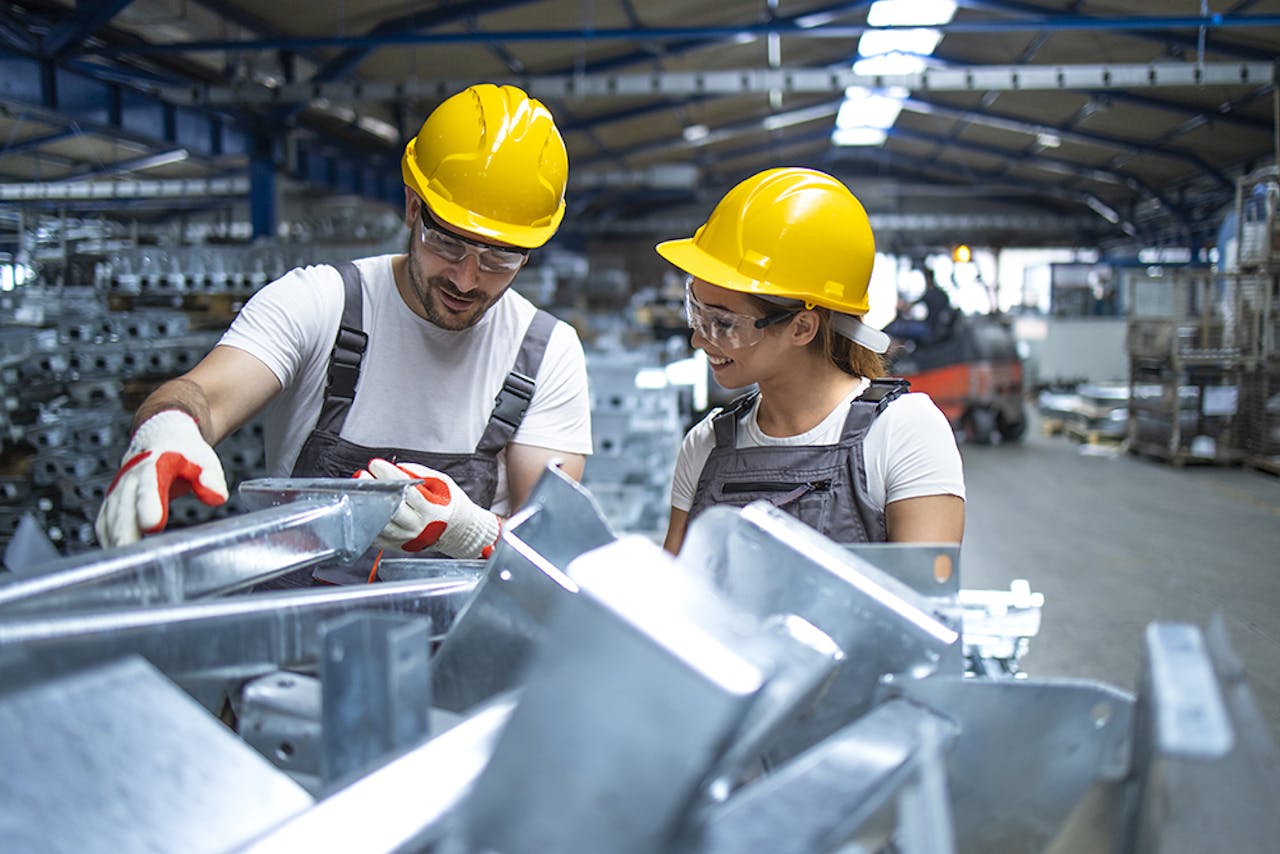

Compression Limiters Manufacturing
Our compression limiters are produced using brass, aluminum, stainless steel, or steel and can be produced with or without a variety of plating finishing options as well as optional quality certifications. Review our capabilities here.
Have a specific question about compression limiter manufacturing? Ask an MW expert.
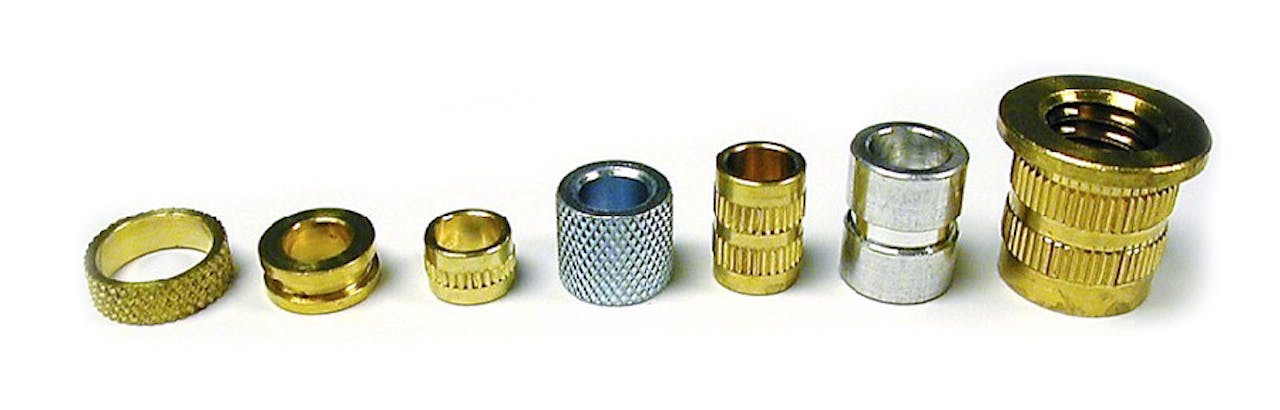

Quality Materials
MW produces compression limiters made from a variety of standard and specialty materials. Some examples of commonly requested materials used to make these products include the following:
Certifications
Common Compression Limiter Configurations
-
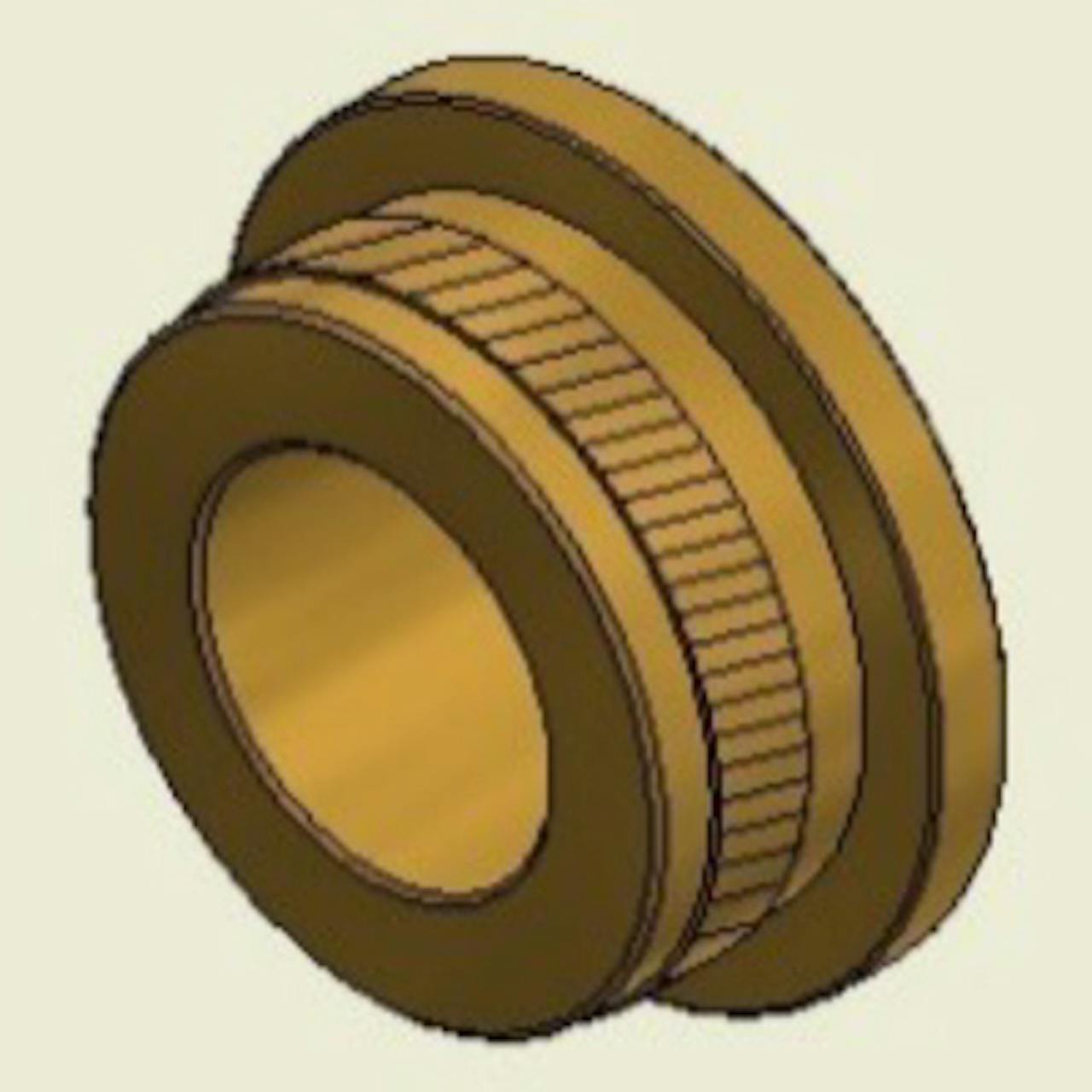 Flanged - Short
Flanged - ShortDesigned for ultrasonic, thermal, press-in, or mold-in installation methods. The flange provides a larger bearing surface/contact area and also acts as a washer.
-
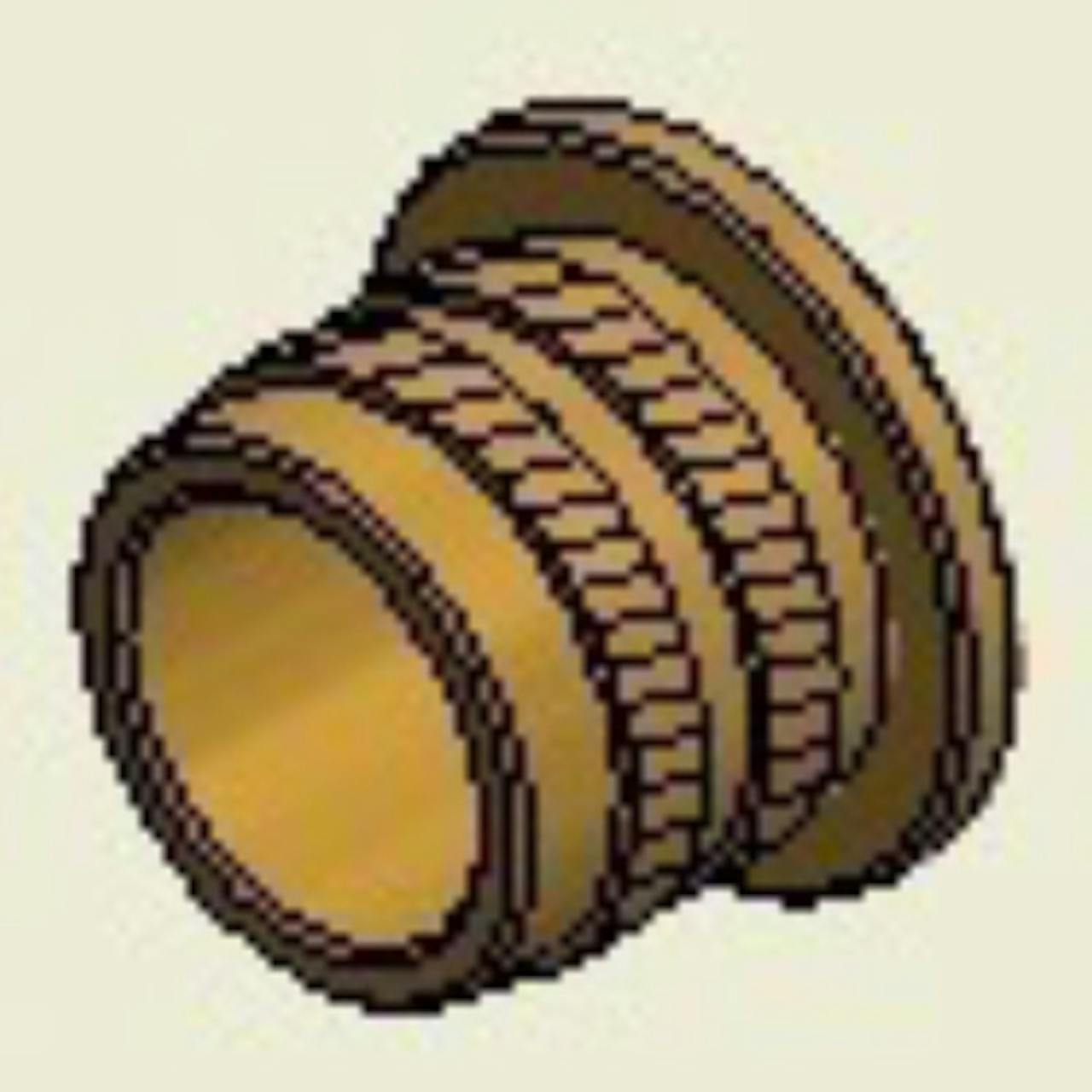 Flanged - Long
Flanged - LongDesigned for ultrasonic, thermal, press-in, or mold-in installation methods. The flange provides a larger bearing surface/contact area and also acts as a washer.
-
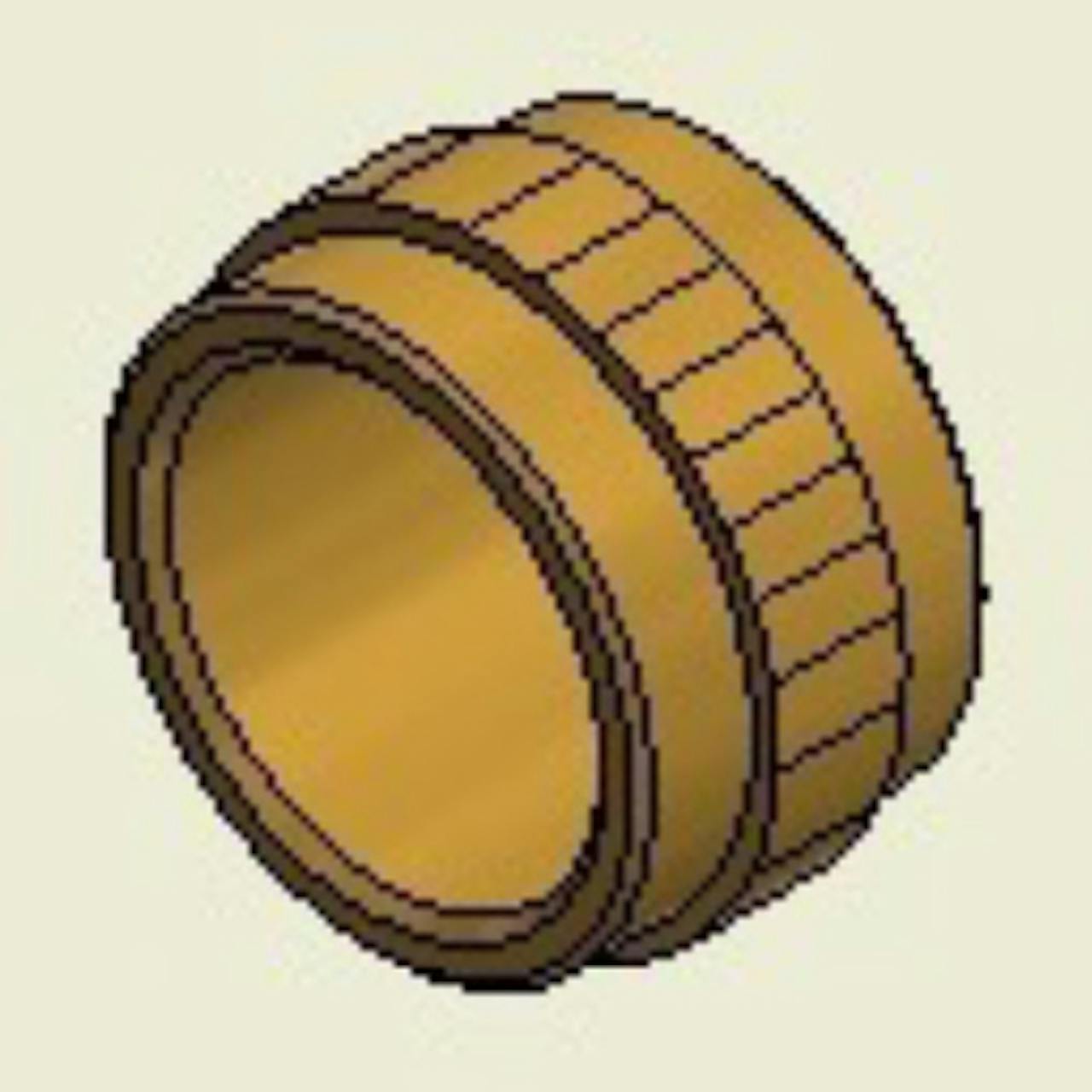 Symmetrical - Short
Symmetrical - ShortDesigned for ultrasonic, thermal, press-in, or mold-in installation methods. It has a straight or diagonal knurl and is symmetrical in design so it can be installed either way without orientation into the hole or onto the core pin.
-
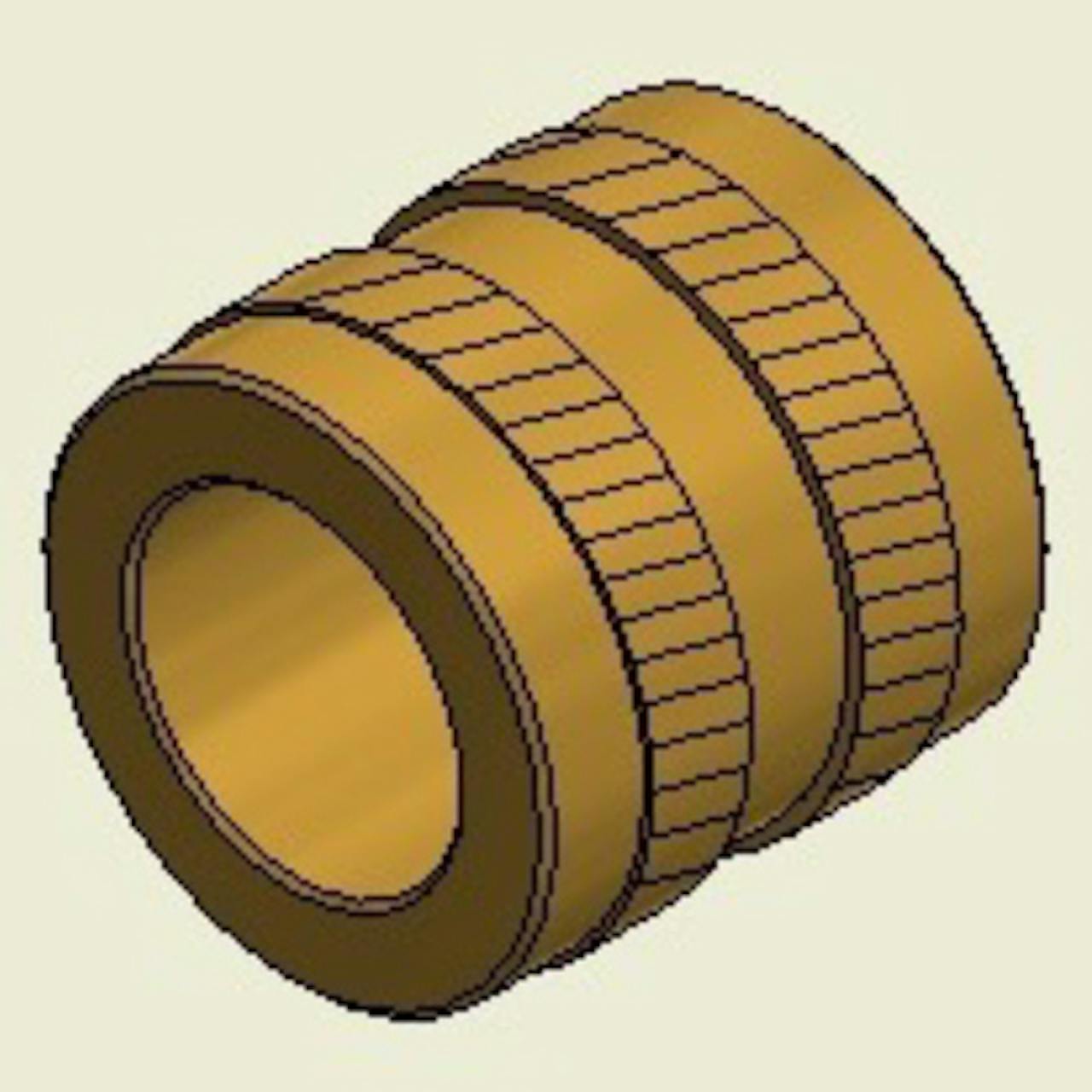 Symmetrical - Long
Symmetrical - LongDesigned for ultrasonic, thermal, press-in, or mold-in installation methods. It has a straight or diagonal knurl and is symmetrical in design so it can be installed either way without orientation into the hole or onto the core pin.
-
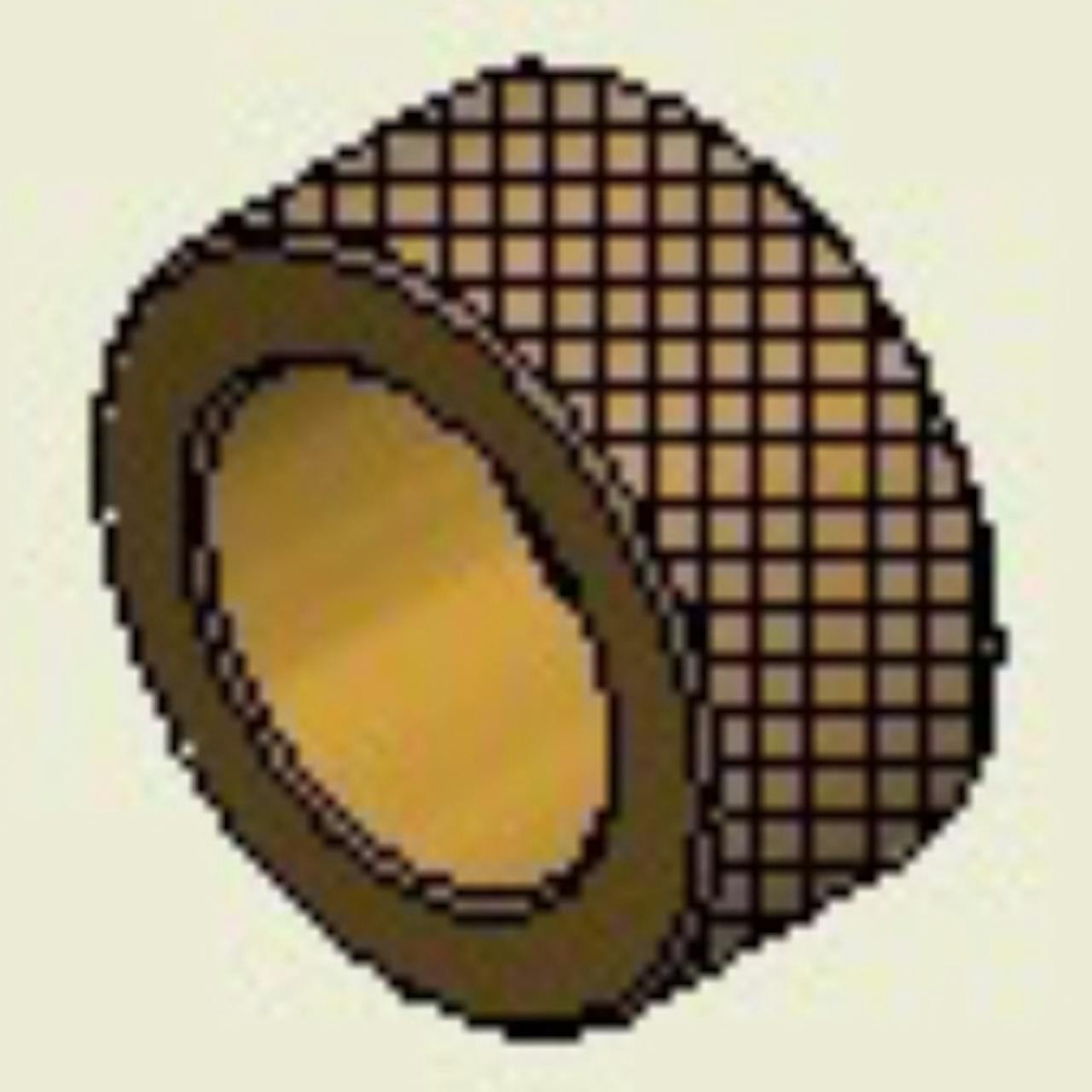 Full Diamond Knurled
Full Diamond KnurledDesigned for mold-in installation only. The diamond knurled design allows the plastic to fill in the peaks and valleys to lock the insert in place. This style also resists tensile loads and also provides added torque resistance compared to non-knurled styles. The part is symmetrical and requires no orientation.
-
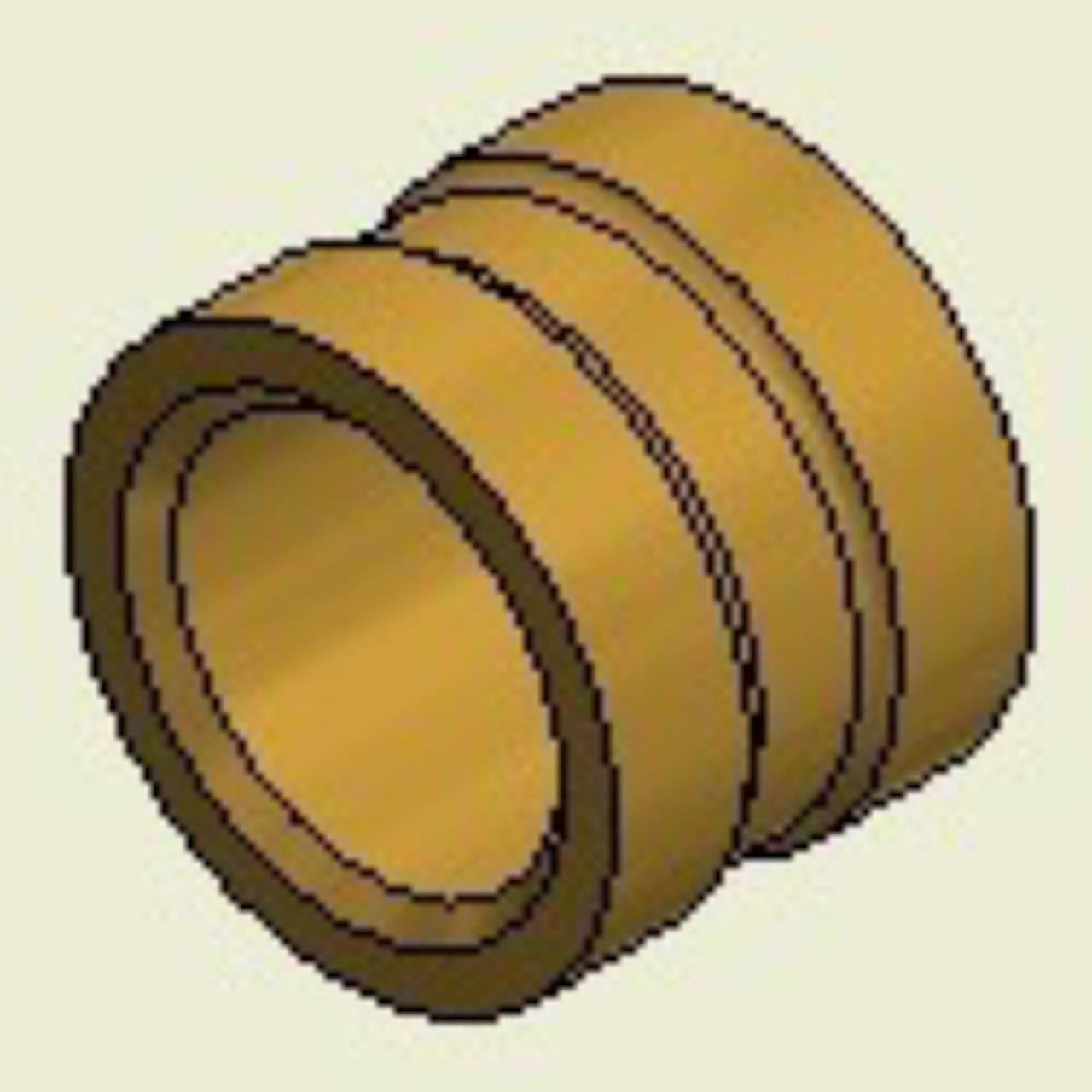 Non-Knurled Symmetrical Mold-In
Non-Knurled Symmetrical Mold-InDesigned for mold-in installation only. The undercut feature allows for plastic fill, therefore providing resistance to tensile loads. If any rotational torque loads are present consider a knurled design for added resistance. The part is symmetrical and requires no orientation.
Compression Limiter Installation Methods
Press In: This method assumes that no melting of the plastic takes place. The insert (compression limiter) is pressed in place with a pre-determined amount of interference to the hole.
Mold In: This method assumes the part will be placed onto a core pin in the mold and the plastic will be molded around the part.
Thermal Insertion: During this process, the insert (compression limiter) is placed into a molded or drilled hole that is slightly smaller than the main diameter of the insert. A heated probe then contacts the insert, causing the plastic to melt in a localized area around the insert. The insert is driven to the required depth or slightly below to allow for a slight withdrawal that may occur. The probe is then removed and the plastic re-solidifies around the insert. This process provides similar results when compared to ultrasonic insertion but utilizes “heat” rather than ultrasonic energy to melt the plastic.
Ultrasonic Insertion: During this process, an insert is placed into a molded or drilled hole that is slightly smaller than the main diameter of the insert. Ultrasonic energy is applied to the insert with the use of an ultrasonic welder and a hardened steel or titanium horn. The ultrasonic energy develops frictional heat at the interface of the insert and plastic. This causes localized melting of the plastic while the insert is driven to the required depth. The plastic then re-solidifies, and the insert is secured in place.
Other Fastener Products
Have Questions?
Talk with our experts today and let us help you figure out the best solution.